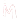06:60:20
Description
fertilizer with an NPK ratio of 06-60-20 is high in phosphorus and potassium, making it well-suited for promoting root development, flowering, fruiting, and overall plant health. However, it's important to consider specific crop requirements, soil conditions, and nutrient management practices when using fertilizers to ensure optimal results and prevent nutrient imbalances.
Mode of Action
Nitrogen (N): The first number in the ratio represents the percentage of nitrogen in the fertilizer. In this case, it's 6%. Nitrogen is essential for various plant functions, including chlorophyll formation, protein synthesis, and overall growth and development. A fertilizer with 6% nitrogen content can provide a moderate amount of nitrogen to support plant growth and promote green, leafy growth. Phosphorus (P): The second number in the ratio represents the percentage of phosphorus in the fertilizer. In this case, it's 60%. Phosphorus is crucial for root development, flowering, and fruiting in plants. A fertilizer with 60% phosphorus content is high in phosphorus, making it suitable for promoting strong root growth, blooming, and fruit set in flowering and fruiting plants. Potassium (K): The third number in the ratio represents the percentage of potassium in the fertilizer. In this case, it's 20%. Potassium is essential for overall plant health, stress tolerance, and fruit quality. A fertilizer with 20% potassium content provides a significant amount of potassium to support plant vigor, disease resistance, and fruit development.
Applications
Soil Testing: Before applying any fertilizer, it's essential to conduct a soil test to determine the existing nutrient levels and pH of the soil. Soil testing helps in identifying nutrient deficiencies or imbalances, allowing for targeted fertilizer application. Pre-Planting Application: Incorporate the fertilizer into the soil before planting or sowing seeds. This ensures that the nutrients are available to the plants from the beginning of their growth cycle. Side-Dressing: For established plants, apply the fertilizer as a side-dressing by broadcasting it around the base of the plants. Lightly incorporate the fertilizer into the soil and water thoroughly to facilitate nutrient uptake. Application Rates: Determine the appropriate application rate based on the specific crop's nutrient requirements, soil test results, and recommendations from agricultural experts or extension services. Avoid over-application, as excessive phosphorus or potassium can lead to nutrient imbalances and environmental pollution. Timing: Timing of fertilizer application depends on the growth stage of the plants and their nutrient demands. For phosphorus, it's crucial to apply the fertilizer at planting or during early growth stages to promote root development. Potassium is needed throughout the growing season, with additional applications during periods of high demand such as flowering and fruiting. Water Management: After fertilizer application, ensure adequate irrigation to facilitate nutrient uptake by the plants. Proper water management helps in dissolving the fertilizer and transporting nutrients to plant roots. Safety Precautions: Follow safety guidelines and precautions mentioned on the fertilizer label. Wear appropriate protective gear such as gloves and eyewear when handling and applying fertilizers. Environmental Considerations: Avoid applying fertilizer near water bodies to prevent nutrient runoff and water pollution. Follow recommended application practices to minimize environmental impact and ensure sustainable agriculture.
| Crop | Common name of the Pest | Dose/acre(gm) | Dilution in Water (Liter) | Waiting Period(Days) |
|---|---|---|---|---|